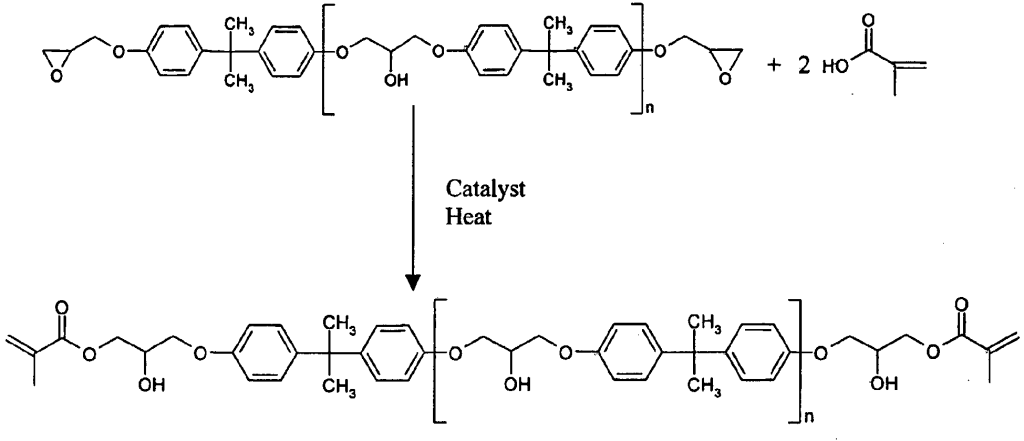
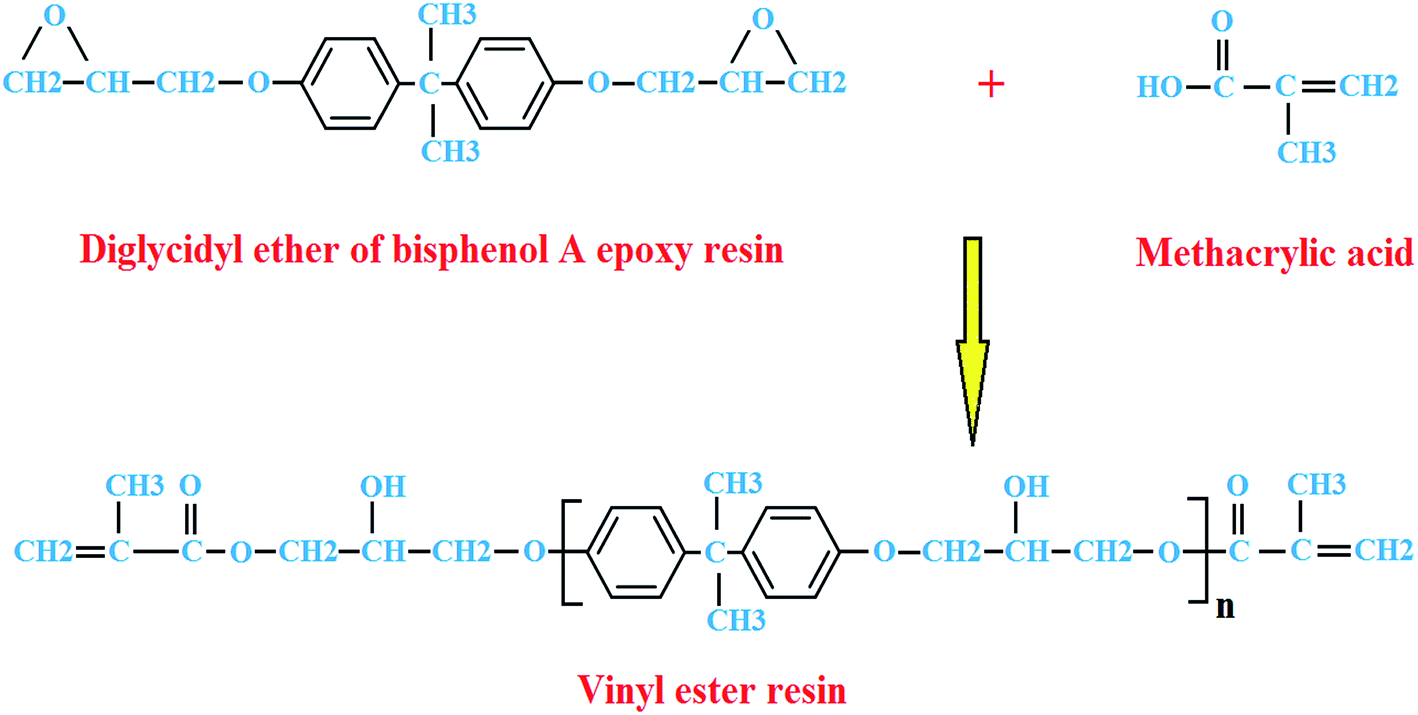
Epoxy Vinyl Ester Resin Structure
Ve resins are a combination of both polyester resin and epoxy resins best properties.
Epoxy vinyl ester resin structure. The molecular structure of vinyl ester resins is similar to that of polyesters but differs primarily on the location of their reactive groups which are positioned only at the ends of the chains. As the length of the chain is available to absorb impact loads this makes vinyl ester resins more durable and resilient than polyesters. Vinyl ester ve resins are thermosetting polymers that combine the good chemical mechanical and thermal properties of epoxy resins with the rapid cure of unsaturated polyester resins ve resins have high chemical and hydrolytic resistances good toughness a high modulus and good thermal and electrical insulation properties. Vinyl ester resins are produced by the reaction esterification between an epoxy resin and an unsaturated monocarboxylic acid.
These resins form durable laminates and. While they have high mechanical strength values similar to epoxy resins they are easy to apply similar to unsaturated polyester resins. The vinyl groups refer to these ester substituents which are prone to polymerize. The diester product is then dissolved in a reactive solvent such as styrene to approximately 35 45 percent content by weight.
Vinyl ester resin or often just vinyl ester is a resin produced by the esterification of an epoxy resin with acrylic or methacrylic acids. Epoxy vinyl ester resins ver are an important class of high performance thermoset molding resins. Bisphenol a based epoxy vinyl ester resins provide high chemical resistance and mechanical strength. Essentially they comprise a base of polyester resin strengthened with epoxy molecules in the backbone of the molecular chain.