Esri Rubber Sheeting
It is slightly faster and produces good results when you have many rubbersheet links spread uniformly over the data.
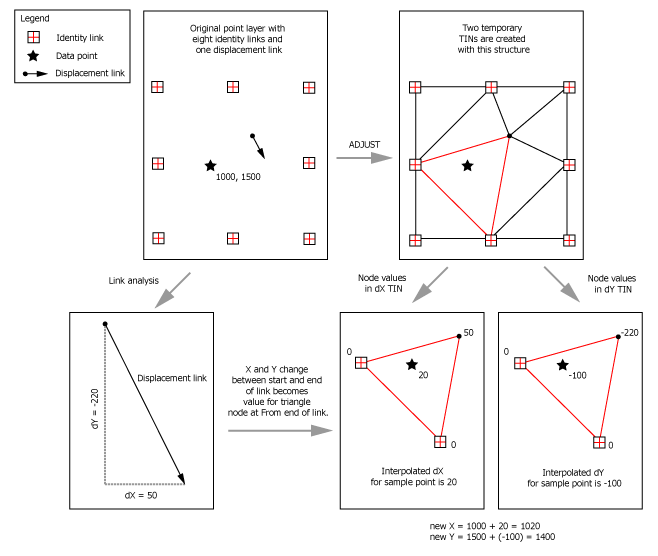
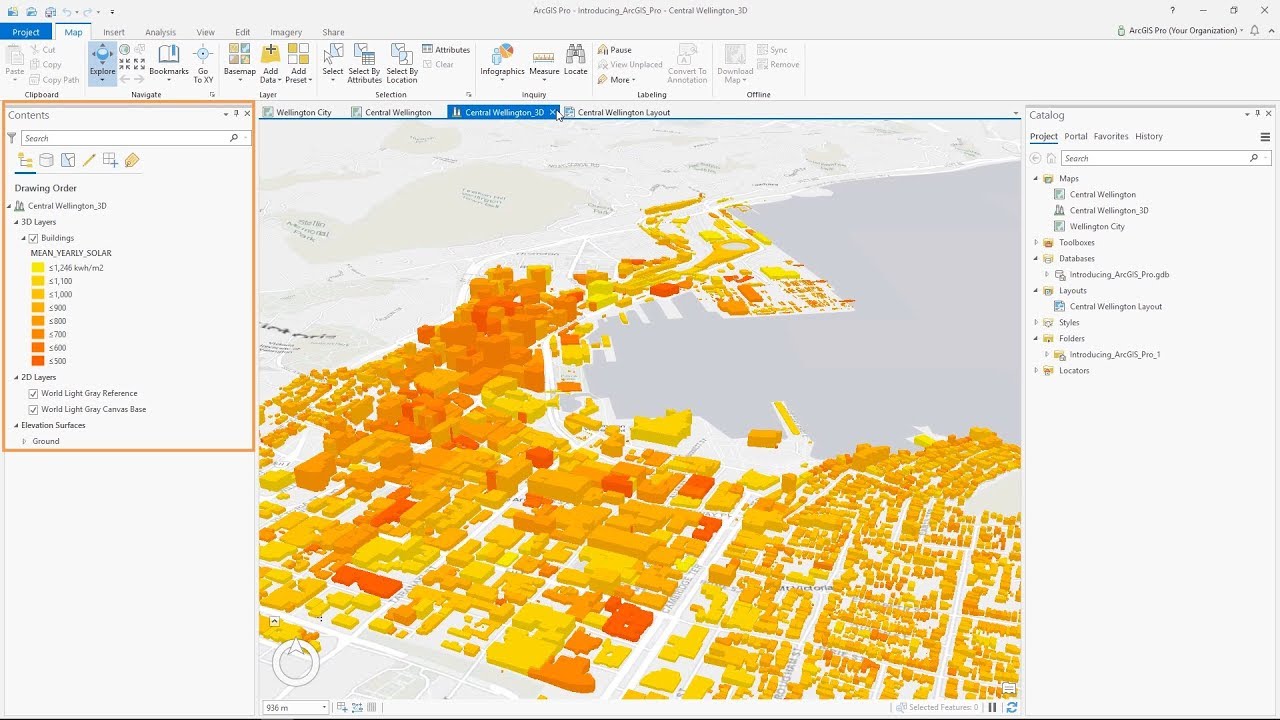
Esri rubber sheeting. Rubbersheeting makes spatial adjustments to align the input feature locations with more accurate target feature locations based on the specified rubbersheet links. The method parameter determines the interpolation method used to create the temporary tins in rubbersheeting. The following is a summary of the command sequence that should be used when rubber sheeting two or more coverages. Editing coverages tables with arcedit the adjust command in the arcedit command reference and understanding gis.
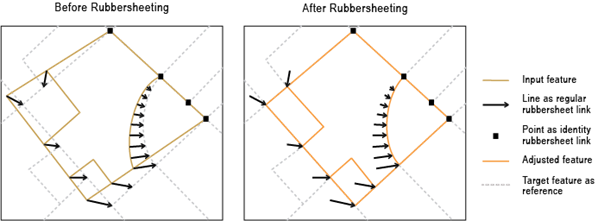
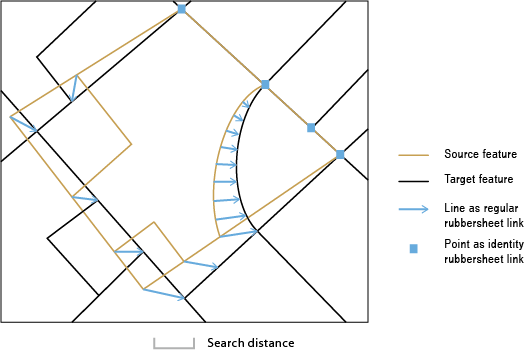
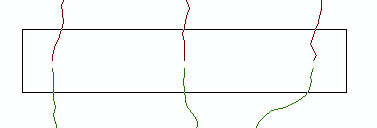
The source layer drawn with solid lines is adjusted to the more accurate target layer. For conceptual and detailed usage information refer to. This tool is intended to be used following the generate rubbersheet links tool. In rubbersheeting adjustments you are usually trying to align one layer with another that is often in close proximity.
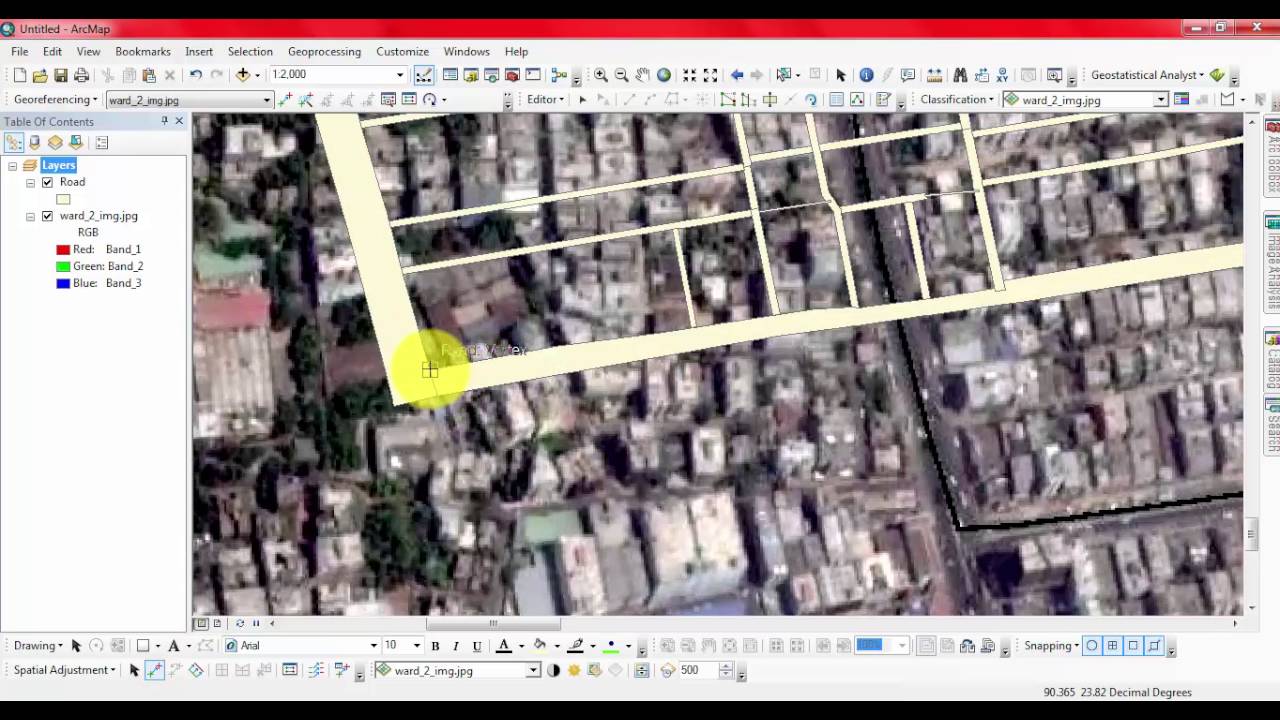
Rubber sheeting is a useful technique in historical gis where it is used to digitize and add old maps as feature layers in a modern gis. See about spatial adjustment rubbersheeting for more details. The source layer drawn with solid lines is adjusted to the more accurate target layer. Rubbersheeting is used to make small geometric adjustments in your data usually to align features with more accurate information.
In rubbersheeting adjustments you are usually trying to align one layer with another that is often in close proximity. Rubbersheeting is used to make small geometric adjustments in your data usually to align features with more accurate information. Before aerial photography arrived most maps were highly inaccurate by modern standards. Linear this method creates a quick tin surface but does not really take into account the neighborhood.
About rubbersheeting rubbersheeting is typically used to align two or more layers.