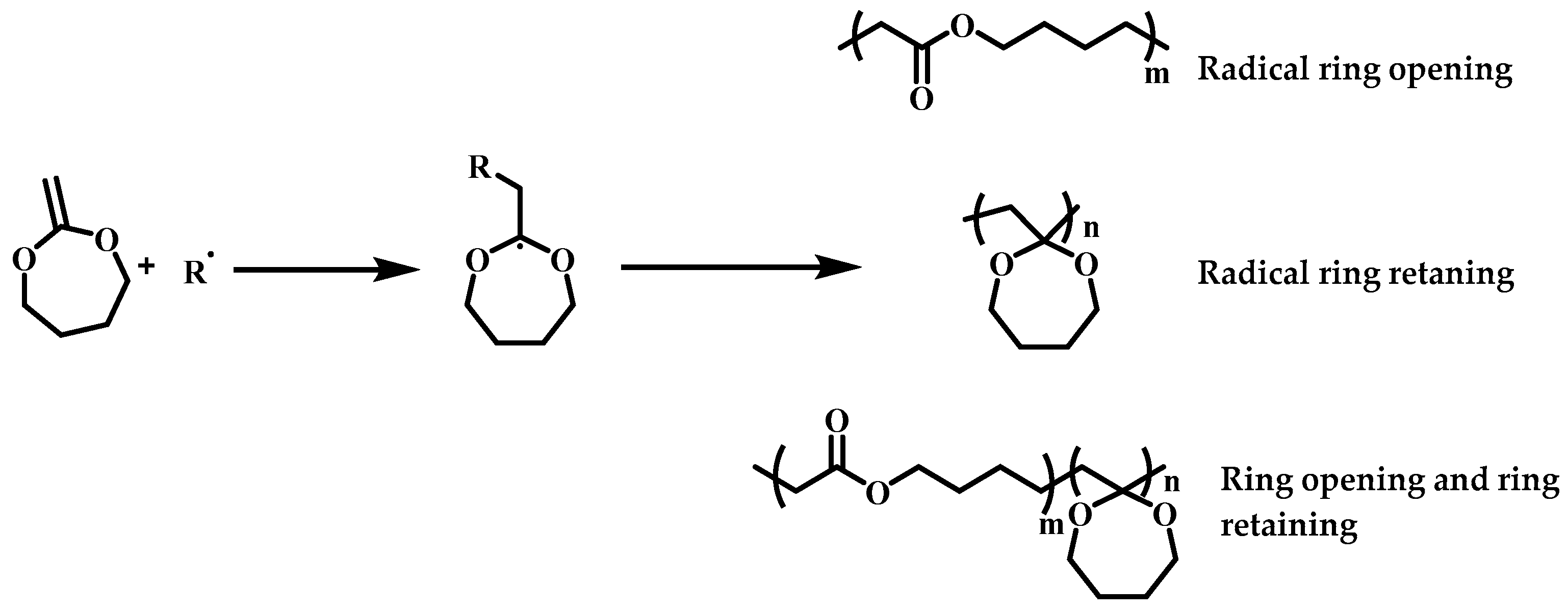
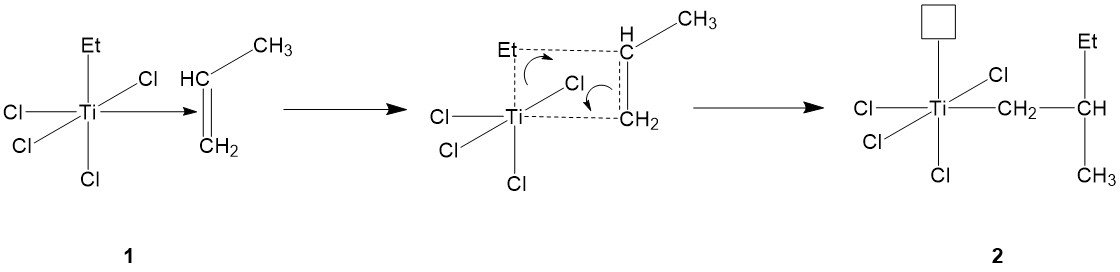
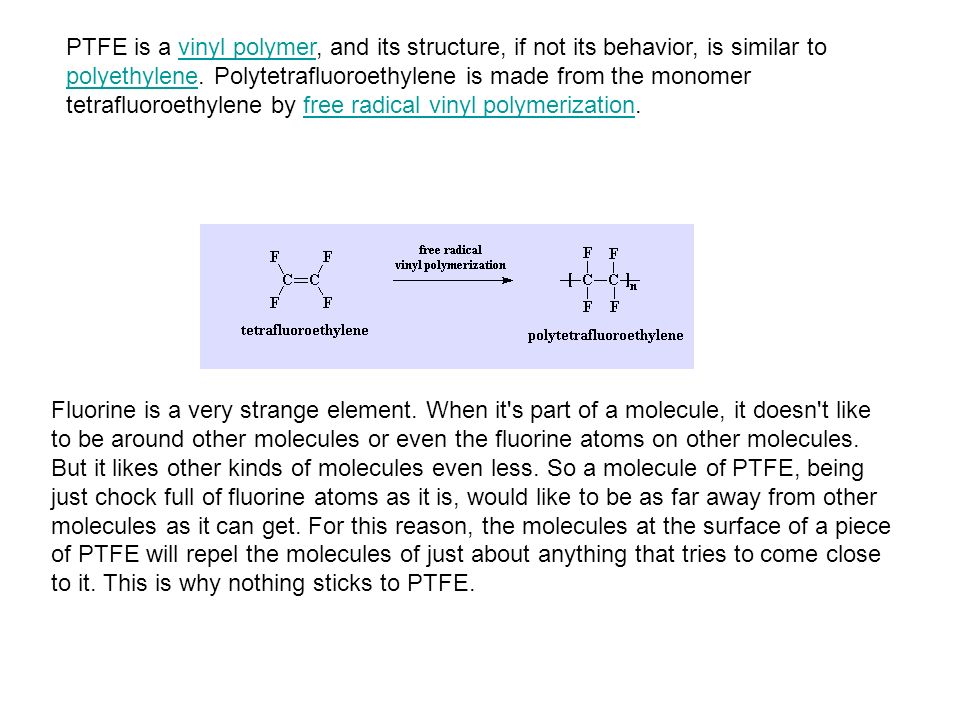
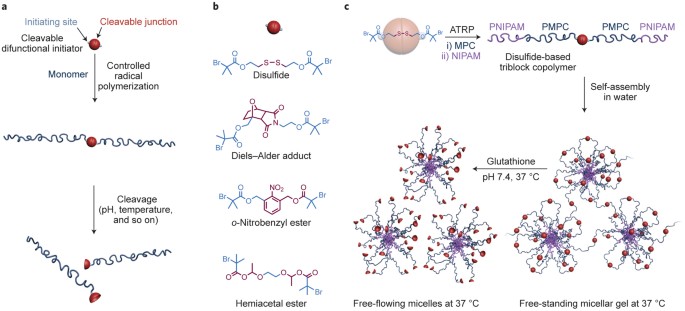
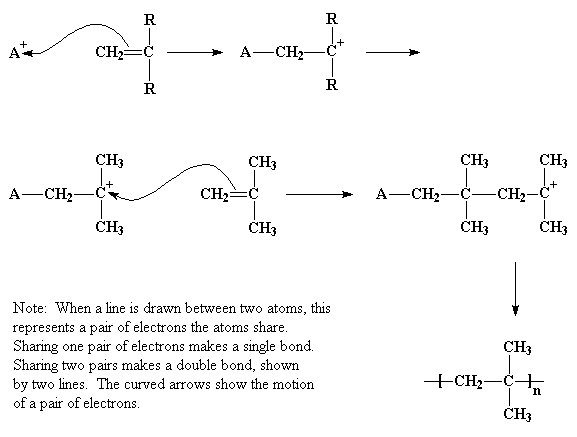Free Radical Vinyl Polymerization Mechanism

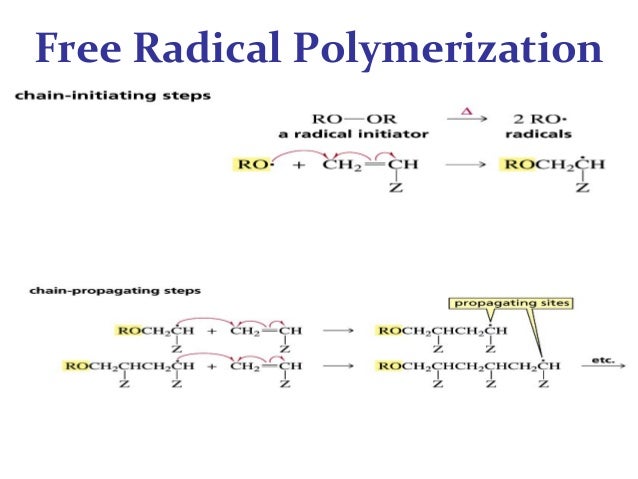
Free radicals can be formed by a number of different mechanisms usually involving separate initiator molecules.
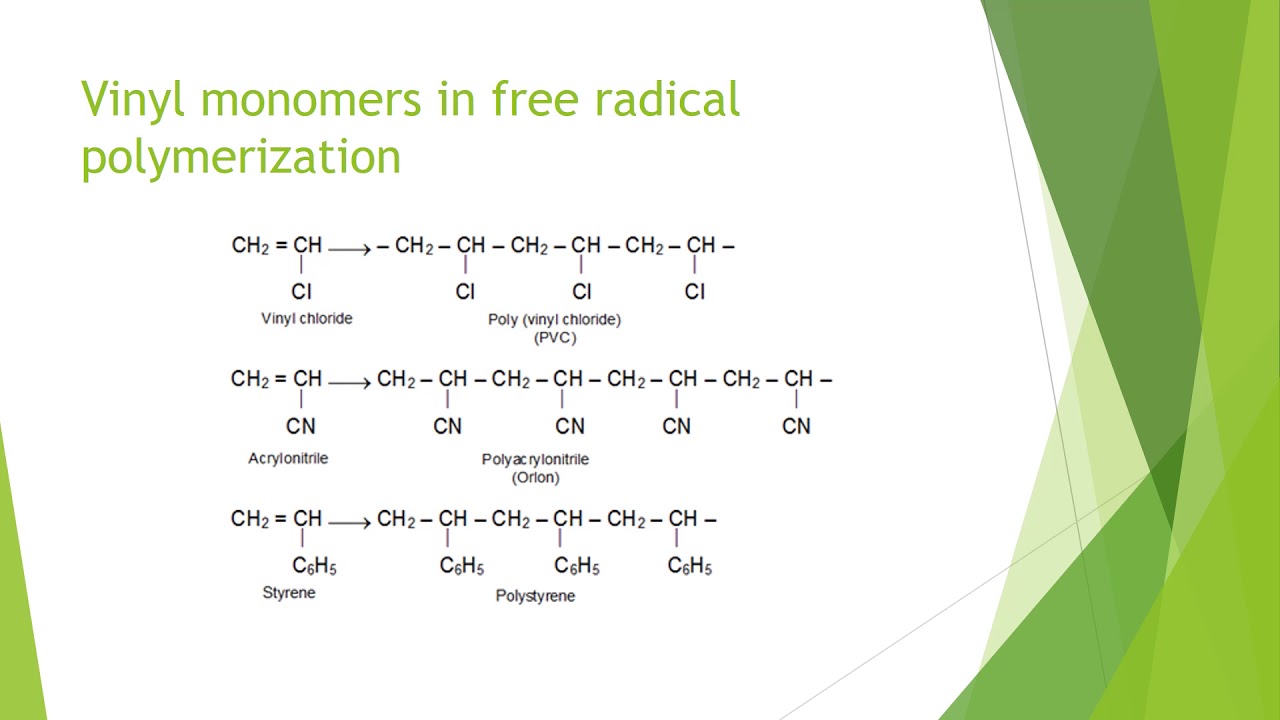
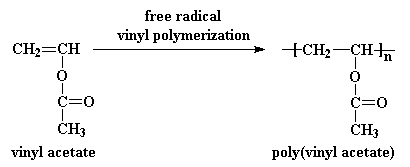
Free radical vinyl polymerization mechanism. It is used to make polymers from vinyl monomers. Mechanism of polymerization of methyl methacrylate mma was studied by means of isotope effects. Free radical polymerization of vinyl monomers. Virtually all of the monomers described above are subject to radical polymerization.
One of the most common and useful reactions for making polymers is free radical polymerization. 99 natural abundance of 13 c kinetic isotope was applied to compare mechanisms of free. It is used to make polymers from vinyl monomers that is from small molecules containing carbon carbon double bonds. R m rm.
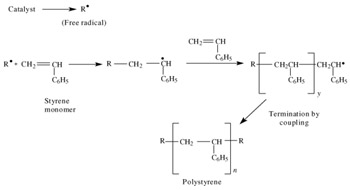
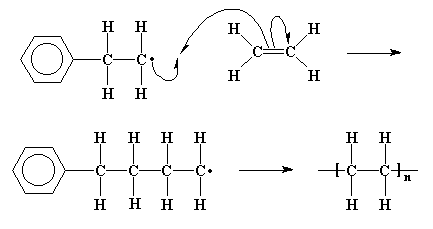
Mechanism of free radical polymerization. Explains the process in polymer science known as free radical vinyl polymerization. Following its generation the initiating free radical adds nonradical monomer units thereby growing the polymer chain. Covalent bond free radical.
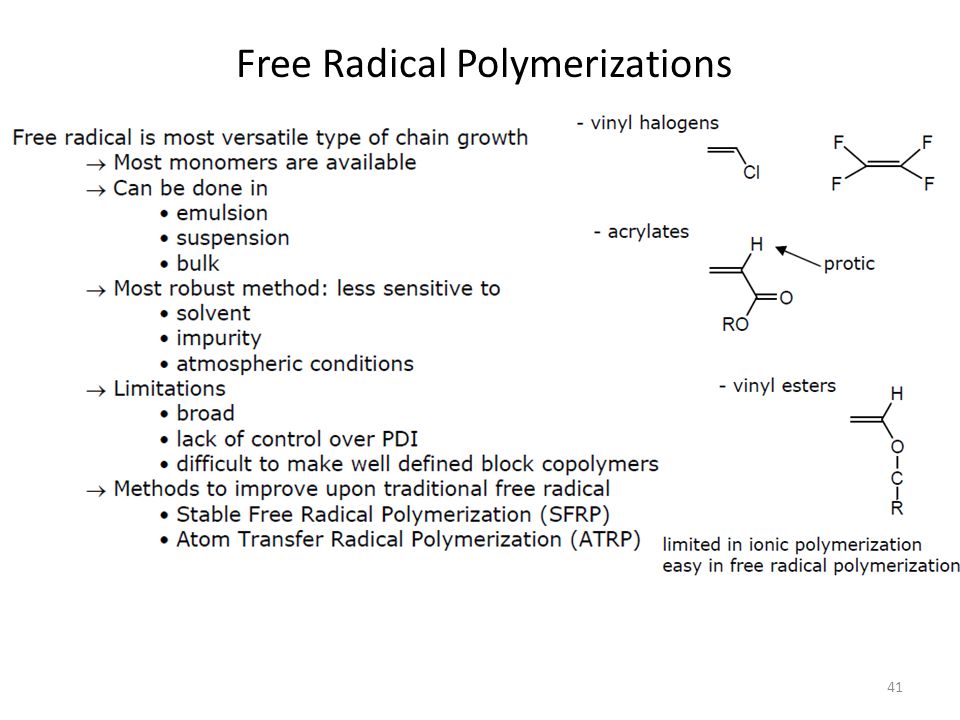
Free radical polymerization is one of the most frequently used techniques in bioprinting to create chemically cross linked hydrogels. Free radical polymerization frp is a method of polymerization by which a polymer forms by the successive addition of free radical building blocks. Photo induced polymerization can be broadly divided based on the initiation mechanism as radical cationic and anionic photopolymerization. Keywords covalent bond free radical.
That is from small molecules containing carbon carbon double bonds. 6 3 2 1 free radical polymerization. Free radical polymerization frp is one of the most important synthesis routes for obtaining vinyl polymers. Following its generation the free radical then reacts with a vinyl monomer that is it adds to one of the electrons of the double bond of the vinyl monomer and the remaining electron becomes the new free radical.
Into free radical polymerization of vinyl acrylate. Explains the process in polymer science known as free radical vinyl polymerization. Deuterium isotope effect of cobalt porphyrin catalysed chain transfer in mma free radical polymerization was determined as the ratio of rate constants for reactions of perdeuterated or not deuterated monomer. Since this can be initiated by traces of oxygen or other minor impurities pure samples of these compounds are often stabilized by small amounts of radical inhibitors to avoid unwanted reaction.